As The Firm In The Diagram Expands From Plant Size 1 To Plant Size 3 It Experiences
As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size 1 to plant size 3 it experiences. Returns to scale have an inverse.
B economies of scale.
As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size 1 to plant size 3 it experiences. As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size 1 to plant size 3 it experiences. More specifically optimum or best firm is considered as one that has set up a plant with lowest possible cost and is also operating it at its lowest average cost point. As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size 3 to plant size 5 it experiences.
B to produce 130 units the firm will choose plant size 2 since its atc is lower for size 2 in producing between 80 and 240 units. C diseconomies of scale. The above diagram shows the short run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm.
Economies of scale suppose that a business incurred implicit costs of 500000 and explicit costs of 5 million in a specific year. The optimum firm refers to the best or ideal size of the firm. As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size 1 to plant size 3 it experiences.
As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size 3 to plant size 5 it experiences. B economies of scale. The concept of optimum firm in economics.
As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size 1 to plant size 3 it experiences. This shape depends on the returns to scale. It helps the firm decide the size of the plant for producing the desired output at the least possible cost.
As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size 3 to plant size 5 it experiences diseconomies of scale. We know that as a firm expands the returns to scale increase. As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size 1 to plant size 3 it experiences.
The short run average total cost curve is u shaped because. A to produce 50 units the firm will choose plant size 1 since its atc is lower for this size firm in producing less than 80 units. As the firm in the diagram on the handout expands from plant size 1 to plant size 3 it experiences.
C diseconomies of scale. Then they remain constant for some time and eventually decrease. Average fixed costs decline continuously as output increases.
It is important to explain the concept of optimum firm. D constant returns to scale.
Chapter 6 Price Elasticity Of Demand
 Elisabeth C Miller Library Gardening Answers Search Results For
Elisabeth C Miller Library Gardening Answers Search Results For
Chapter 6 Price Elasticity Of Demand
 Econ 202s Test 2 Chapter 6 Economics 202s With Colburn At Old
Econ 202s Test 2 Chapter 6 Economics 202s With Colburn At Old
 As The Firm In The Above Diagram Expands From Plant Size 3 To Plant
As The Firm In The Above Diagram Expands From Plant Size 3 To Plant
 Nucor Nue Set To Expand Sheet Steel Plant In Kentucky Nasdaq Com
Nucor Nue Set To Expand Sheet Steel Plant In Kentucky Nasdaq Com
Elisabeth C Miller Library Gardening Answers Search Results For
 Pdf Hydrangea Production Cultivar Selection And General Practices
Pdf Hydrangea Production Cultivar Selection And General Practices
 The Floor Board Blog Valenti Flooring
The Floor Board Blog Valenti Flooring
 Trauma Airway Management Chapter 3 Trauma Anesthesia
Trauma Airway Management Chapter 3 Trauma Anesthesia
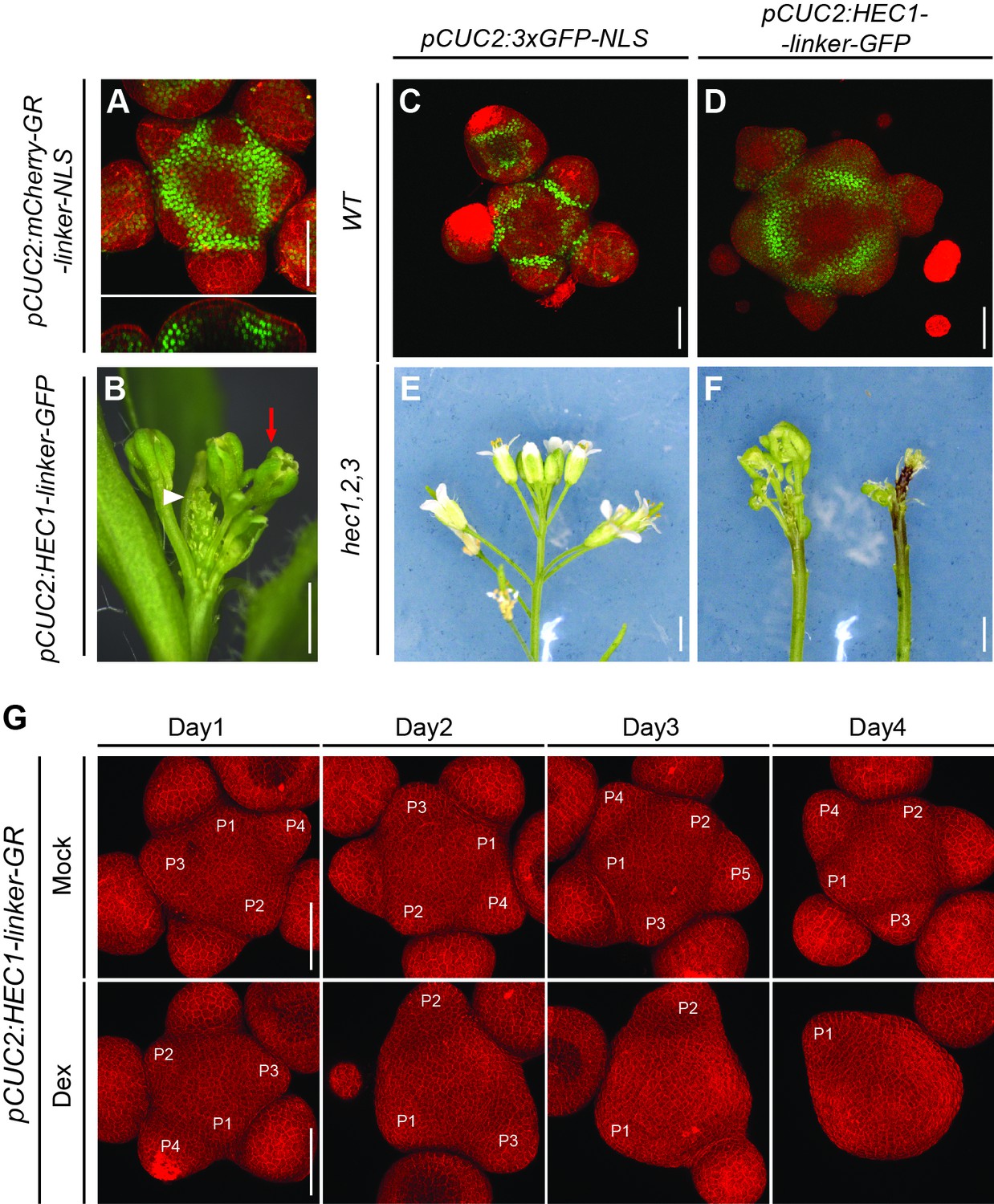 Control Of Plant Cell Fate Transitions By Transcriptional And
Control Of Plant Cell Fate Transitions By Transcriptional And
 The Above Diagram Shows The Short Run Average Total Cost Curves For Five
The Above Diagram Shows The Short Run Average Total Cost Curves For Five
 Setting And Vetting Strategy Bridging The Chasm Between Ceos And
Setting And Vetting Strategy Bridging The Chasm Between Ceos And
 Econ 202s Test 2 Chapter 6 Economics 202s With Colburn At Old
Econ 202s Test 2 Chapter 6 Economics 202s With Colburn At Old
 The Above Diagram Shows The Short Run Average Total Cost Curves For Five
The Above Diagram Shows The Short Run Average Total Cost Curves For Five
Building A Community Garden In Your Park Grow Your Park Initiative
0 Response to "As The Firm In The Diagram Expands From Plant Size 1 To Plant Size 3 It Experiences"
Post a Comment