In The Diagram Where Is The Mastoid Process
It is also filled with sinuses or mastoid cells. Parts of the frontal and sphenoid bones comprise the roof of the orbit.
 Mastoidectomy To Treat Cholesteatoma Or Ear Infection
Mastoidectomy To Treat Cholesteatoma Or Ear Infection
This article covers the anatomy of the temporal bone its parts connecting sutures and foramina.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/5471/e7edZa4izRPlbDSqDu4qA_digastric_muscle_posterior_belly.png.jpeg)
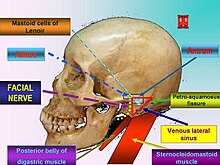
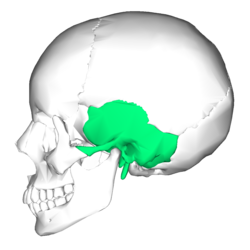
In the diagram where is the mastoid process. Parts of the zygomatic and sphenoid bones form the lateral wall of the orbit. Structure and landmarks of the temporal bone. The mastoid process is part of the temporal bone the large bone that runs along the middle bottom of the skull.
The mastoid process is a point of attachment for the sternocleidomastoid muscles of the neck. The mastoid process is a small triangular shaped bone that protrudes from either side at the base of your skull. The mastoid notch is located medial to the mastoid process.
It is the prominent bony protrusion easily seen behind the earlobes. The main function of the mastoid process is to connect your neck muscles to your skull and help regulate pressure in your ear. Click now to learn more at kenhub.
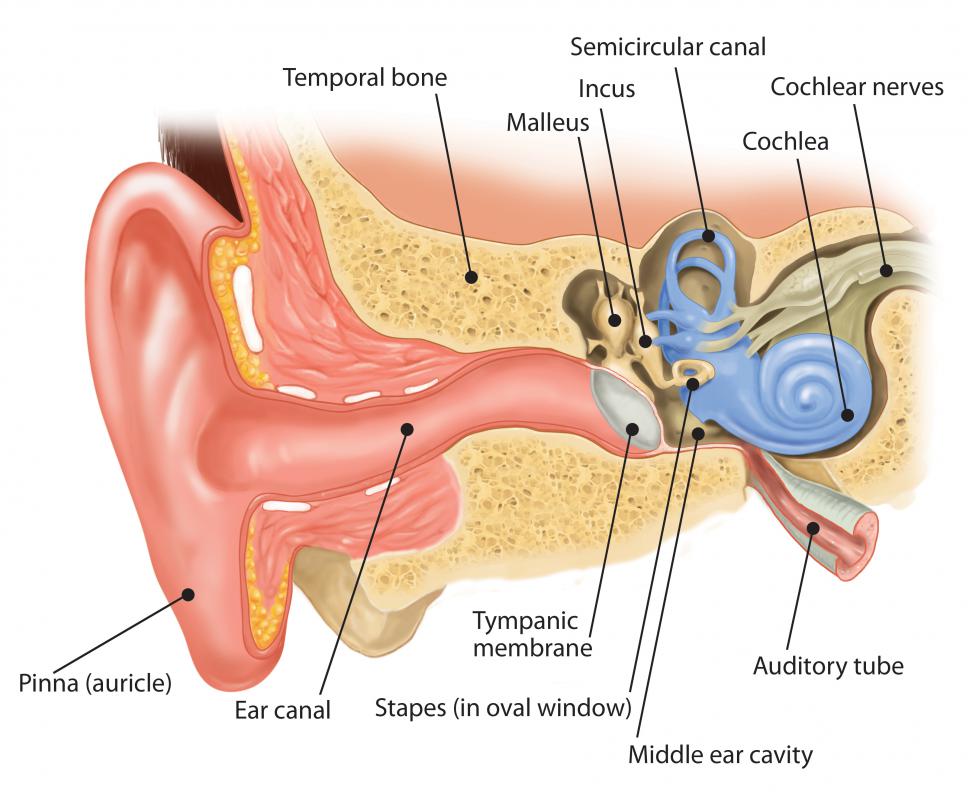
The mastoid process is located just behind the ear canal and lateral to the styloid process. The mastoid is connected to the part of the ear where the hearing and balance mechanisms are located. The mastoid can be affected by diseases such as infection and cholesteatoma.
This article covers the anatomy function muscle attachments and clinical aspects of the mastoid process. Small fragile bone making up part of the front inner walls of each eye socket and providing room for the passage of the lacrimal ducts. The air cells are lined by a thin mucous membrane.
There is a deep groove on the medial side of the process as well as a shallow furrow called occipital groove which houses the occipital artery. The mastoid is a honeycomb of air cells located behind the ear. Parts of the maxilla lacrimal ethmoid and sphenoid bones form the medial wall of the orbit.
Parts of the maxilla zygomatic and palatine bones make up the floor of the orbit. The mastoid process serves for the attachment of the sternocleidomastoid the posterior belly of the digastric muscle splenius capitis and longissimus capitis. You can locate your mastoid if you place your fingers behind your earlobe.
Mastoid notch serves as the site of muscle attachment for the anterior and posterior bellies of the digastrics whose function is to open the mouth 2. Ear infections linked to mastoid cells is typically treated with antibiotics. The mastoid process is located just behind the ear in humans.
Similarly a curved groove known as sigmoid sulcus is present on the inner surface of the bony structure to lodge a part of the transverse sinus. The mastoid process lying in the mastoid part of the temporal bone in the human skull is a conicalpyramidal projection present each side of the head at the base of the skull. It is pierced by stylomastoid foramen in front and mastoid foramen is found on its back.
The bone which forms part of the hard palate of the mouth part of the nasal cavity and part of the orbital cavities.
 Mastoid Bone Picture Human Anatomy Study Pinterest Anatomy
Mastoid Bone Picture Human Anatomy Study Pinterest Anatomy
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/717/p7nvi8of105jRSVvEIXQVg_structure-and-landmarks-of-temporal-bone_english.jpg) Mastoid Process Anatomy Function Attachments Kenhub
Mastoid Process Anatomy Function Attachments Kenhub
 Mastoid Emissary Vein Operative Neurosurgery
Mastoid Emissary Vein Operative Neurosurgery
 Mastoid Process Anatomy Pictures And Information
Mastoid Process Anatomy Pictures And Information
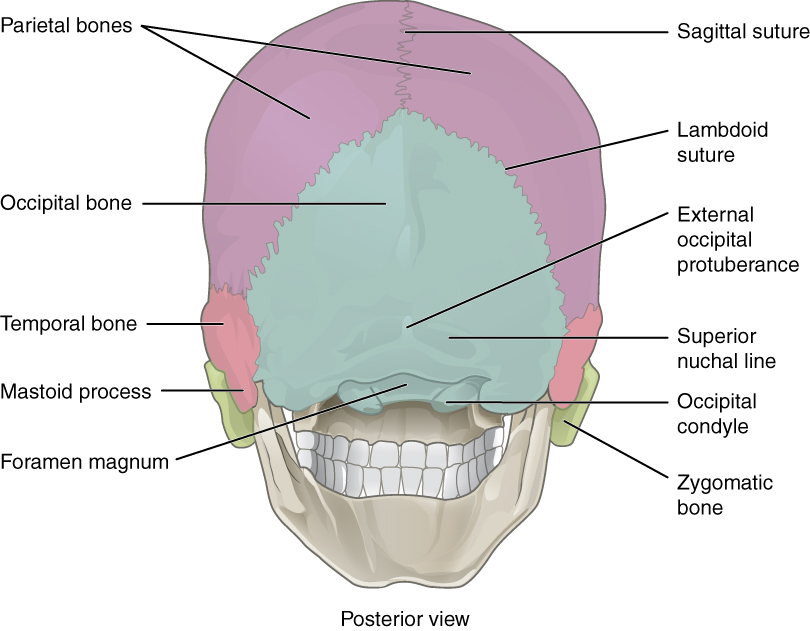 7 2 The Skull Anatomy And Physiology
7 2 The Skull Anatomy And Physiology
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/5471/e7edZa4izRPlbDSqDu4qA_digastric_muscle_posterior_belly.png.jpeg) Mastoid Process Anatomy Function Attachments Kenhub
Mastoid Process Anatomy Function Attachments Kenhub
Diffrentiate Male Skull From Female Skull
 Mastoid Process Stock Photos Mastoid Process Stock Images Alamy
Mastoid Process Stock Photos Mastoid Process Stock Images Alamy
 Mastoid An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Mastoid An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 What Is The Mastoid Process With Pictures
What Is The Mastoid Process With Pictures
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/5467/i69qkAHvcUSvEuXXQsZVTQ_Mastoid_process_01.png.jpeg) Mastoid Process Anatomy Function Attachments Kenhub
Mastoid Process Anatomy Function Attachments Kenhub
 Overview Of The Mastoidectomy To Get Access To The Middle Ear A 1
Overview Of The Mastoidectomy To Get Access To The Middle Ear A 1
 Acupuncture Point Gall Bladder 12 Gb 12 Wangu Mastoid Process
Acupuncture Point Gall Bladder 12 Gb 12 Wangu Mastoid Process
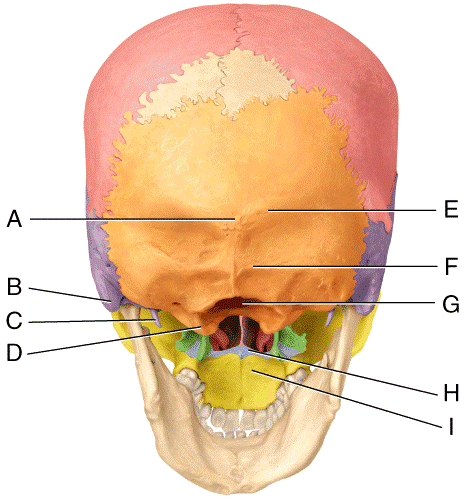 Print Multi Choice The Skeletal System The Axial Skeleton
Print Multi Choice The Skeletal System The Axial Skeleton
Anatomical Landmarks To Avoid Injury To The Great Auricular Nerve
 Posterior Auricular Artery An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Posterior Auricular Artery An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



0 Response to "In The Diagram Where Is The Mastoid Process"
Post a Comment