Refer To The Diagram To The Right The Vertical Difference Between Curves F And G Measures
Refer to figure 4 8. B average fixed cost falls as output rises.
The vertical difference between curves f and g measures marginal costs.
Refer to the diagram to the right the vertical difference between curves f and g measures. F average total cost curve. H average fixed cost curve. H average fixed cost curve.
In that case the diagram shows the effect of a negative externality in the production of a good. The vertical difference between curves f and g measures average fixed costs over the past twenty years the number of small family farms has fallen significantly and in their place there are fewer but larger farms owned by corporations. Curve g approaches curve f because a marginal cost is above average variable costs.
Refer to figure 115. 10 refer to figure 11 1. The economically efficient output is q2.
The vertical difference between curves f and g measures 19 if the marginal cost curve is below the average variable cost curve then a average variable cost is increasing. The difference between nominal gdp and real gdp is that real gdp a. 28 the vertical difference between curves f and g measures a average fixed costs.
C marginal cost must be decreasing. The vertical difference between curves f and g measures 58 a sunk costs. Suppose the current market equilibrium output of q1 is not the efficient output because of an externality.
Show transcribed image text refer to the diagram to the right. D average fixed costs. Econ exam study guide by emilyventuraxo includes 120 questions covering vocabulary terms and more.
D e marginal cost curve. The vertical difference between curves f and g measures marginal costs. The vertical difference between curves f and g measures 18 refer to figure 10 4.
In a diagram that shows the marginal product of labor on the vertical axis and labor on the horizontal axis the marginal product curve 10 a never intersects the horizontal axis. D e marginal cost curve. The vertical difference between curves f and g measures a average fixed costs.
Sign up to view the full version. Is larger than nominal gdp. It is equal to the vertical distance g to q2.
29 curve g approaches curve f because a marginal cost is above average variable costs. B intersects the horizontal axis at a point corresponding to the 5th worker. Chapter 4 aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
This is the end of the preview. G average variable cost curve. B average variable cost is decreasing.
F average total cost curve. Aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves must not be confused with demand and supply curves that we use to represent markets in microeconomics. G average variable cost curve.
If because of an externality the economically efficient output is q2. D the 5th worker is hired. This preview has intentionally blurred sections.
Refer to figure 115.
 Worksheet For Analytical Calibration Curve
Worksheet For Analytical Calibration Curve
 A Biologist S Guide To Statistical Thinking And Analysis
A Biologist S Guide To Statistical Thinking And Analysis
 The Hertzsprung Russell Diagram Hertzsprung Russell Diagram Naap
The Hertzsprung Russell Diagram Hertzsprung Russell Diagram Naap
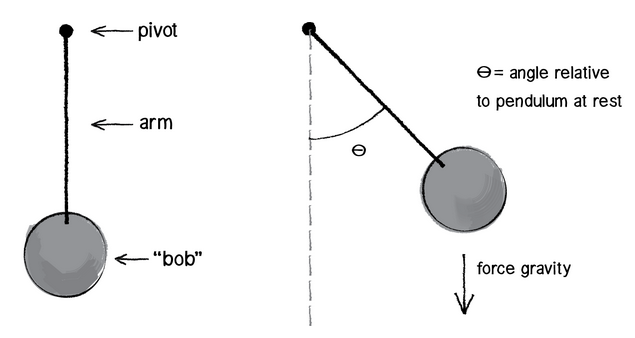
 Trig And Forces The Pendulum Article Khan Academy
Trig And Forces The Pendulum Article Khan Academy
 10 1 Monopolistic Competition Principles Of Economics
10 1 Monopolistic Competition Principles Of Economics
 What Is A Frequency Response Function Frf Siemens Plm Community
What Is A Frequency Response Function Frf Siemens Plm Community
 Supply And Demand Curves In The Classical Model And Keynesian Model
Supply And Demand Curves In The Classical Model And Keynesian Model
 Trig And Forces The Pendulum Article Khan Academy
Trig And Forces The Pendulum Article Khan Academy
 Calculus I Area Between Curves
Calculus I Area Between Curves
 Type Anatomy A Visual Guide To The Parts Of Letters Visual
Type Anatomy A Visual Guide To The Parts Of Letters Visual
 Definition Of Production Possibilities Curve Ppc Chegg Com
Definition Of Production Possibilities Curve Ppc Chegg Com
 Elasticities And Demand Curve Shapes E B F 200 Introduction To
Elasticities And Demand Curve Shapes E B F 200 Introduction To
 Solved Curve G Approaches Curve F Because Marginal Cost I
Solved Curve G Approaches Curve F Because Marginal Cost I
 The Derivative Tangent Line Equations Video Khan Academy
The Derivative Tangent Line Equations Video Khan Academy
 Calculus I Area Between Curves
Calculus I Area Between Curves



0 Response to "Refer To The Diagram To The Right The Vertical Difference Between Curves F And G Measures"
Post a Comment