The Monopolistically Competitive Firm In The Diagram Is
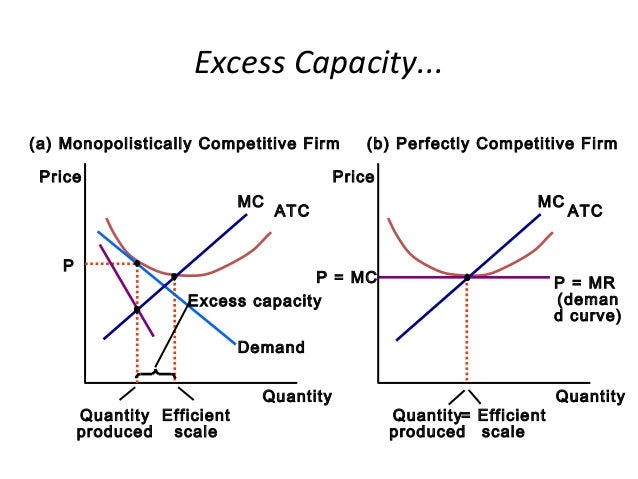
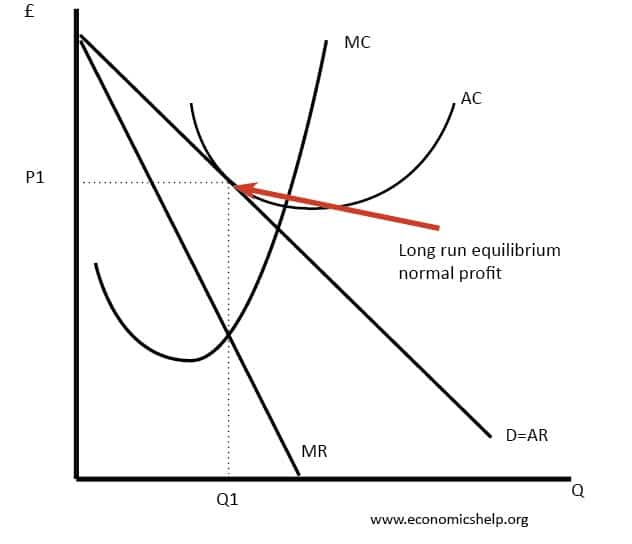
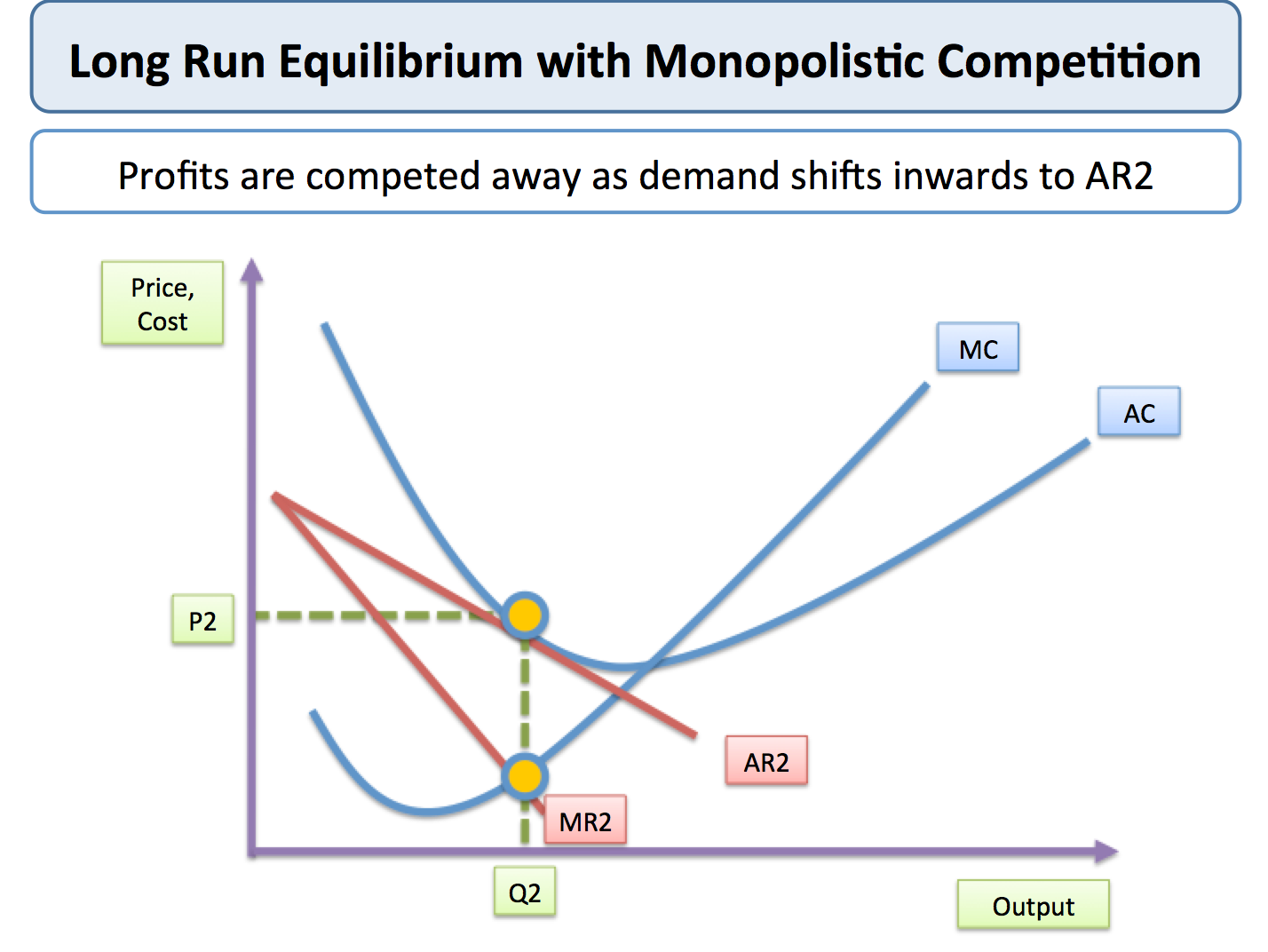
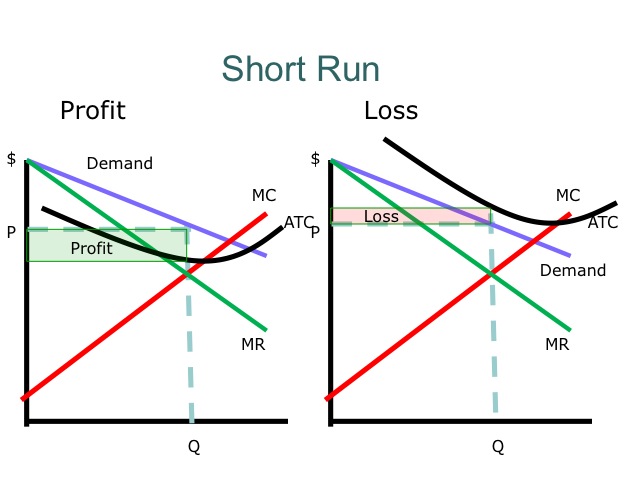
Short run profits and losses and long run equilibrium. The greater the degree of product variation the greater is the excess capacity problem.
 Monopolistic Competition The Four Types Of Market Structure Econo
Monopolistic Competition The Four Types Of Market Structure Econo
The perfectly competitive firm is both allocatively efficient because price mc and productively efficient because the equilibrium output occurs at a level where mc ac.
The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is. A profit maximizing firm in a monopolistically competitive market differs from a firm in a perfectly competitive market because the firm in the monopolistically competitive market a has no barriers to entry. A monopolistically competitive market is productively inefficient market structure because marginal cost is less than price in the long run. On the other hand in monopolistic competition there is an unrestricted entry into and exit from the industry.
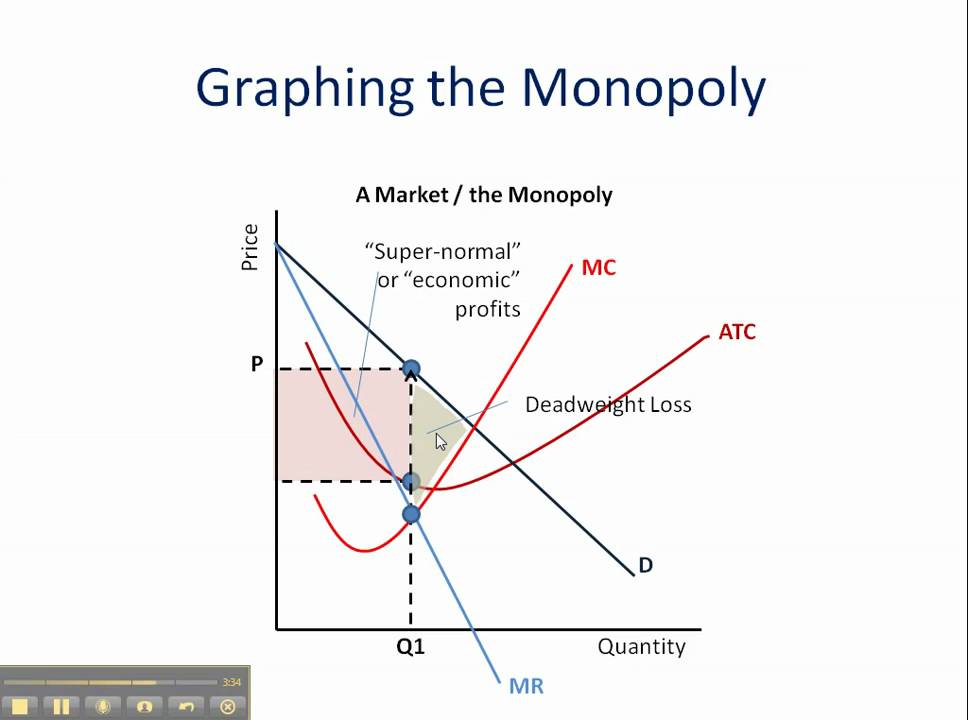
As a single firm regulates the whole market there is no difference between firm and industry in the monopoly. If you look at the other diagram though. Key differences between monopoly and monopolistic competition.
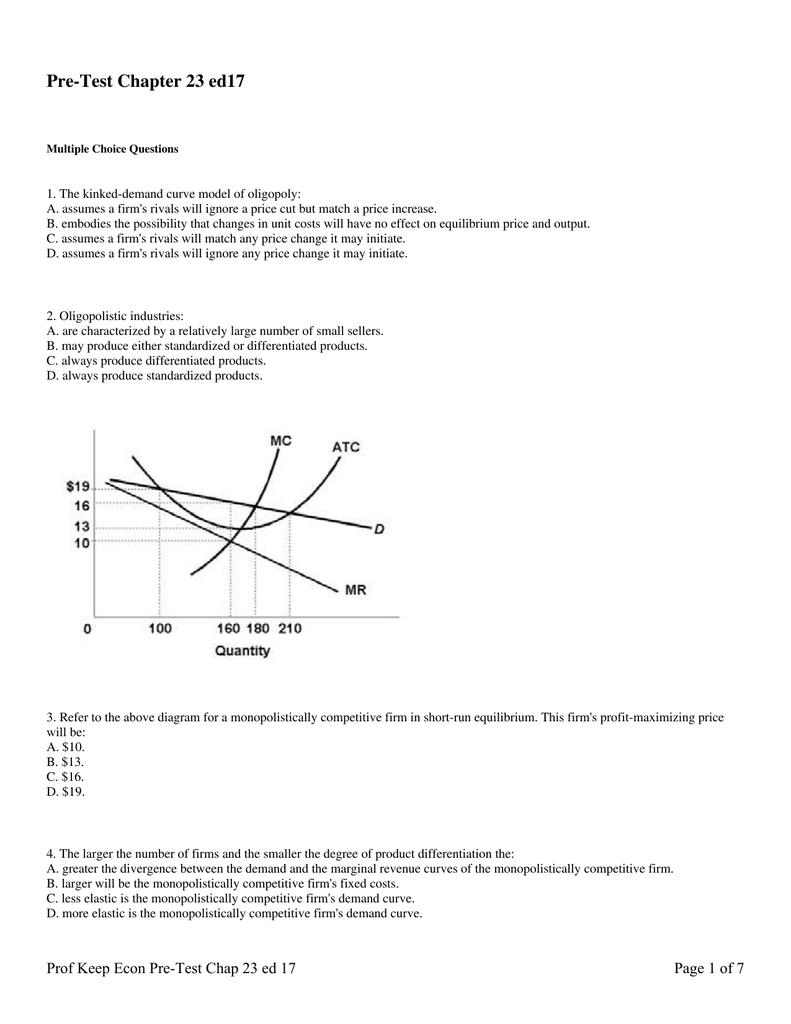
A monopolistically competitive firm is producing at an output level in the short run where average total cost is 350 price is 300 marginal revenue is 150 and marginal cost is 150. In the short run both under monopoly and monopolistic competition the firm can enjoy super normal profits normal profits or can sustain losses. B faces a downward sloping demand curve for its product.
The excess capacity problem means that monopolistically competitive firms typically produce at some point on the rising segment of their average total cost curve. But in the long run firm under monopolistic competition will enjoy only normal profits. The greater the degree of product variation the lesser is the excess capacity problem.
Therefore the equilibrium is at qm pm. Comparisons with the efficient structure of perfect competition. Profit maximisation occurs where mrmc.
The bottom of the ac curve. Usually supernormal profit attracts new firms to enter the market but there are barriers. A monopolistically competitive firm might be said to be marginally inefficient because the firm produces at an output where average total cost is not a minimum.
So it is a single firm industry. Monopoly diagram short run and long run. Point m this diagram shows how a monopoly is able to make supernormal profits because the price ar is greater than ac.
The monopolistically competitive firm illustrated in the diagram exhibits productive inefficiency because its profit maximizing output is not at the intersection of marginal cost and average total cost. Hence monopolistically competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses by producing that quantity where marginal revenue equals marginal cost both over the short run and the long run.
Perfect Competition And Monopolistic Competition Differences
 Short Run And Long Run Equilibrium Monopolistic Competition
Short Run And Long Run Equilibrium Monopolistic Competition
 Monopolistic Competition Tutor2u Economics
Monopolistic Competition Tutor2u Economics
 Monopolistic Competition Definition Diagram And Examples
Monopolistic Competition Definition Diagram And Examples
 The Graph Shows The Costs Revenue And Demand Facing A
The Graph Shows The Costs Revenue And Demand Facing A
Useful Notes On Excess Capacity Under Monopolistic Competition
 13 Monopolistic Competition Ppt Video Online Download
13 Monopolistic Competition Ppt Video Online Download
Monopolistic Competition Course Hero
 Monopoly How To Graph It Youtube
Monopoly How To Graph It Youtube
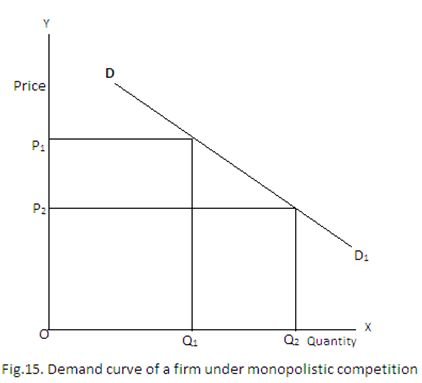 Demand Curve Under Monopolistic Competition Homework Help In
Demand Curve Under Monopolistic Competition Homework Help In
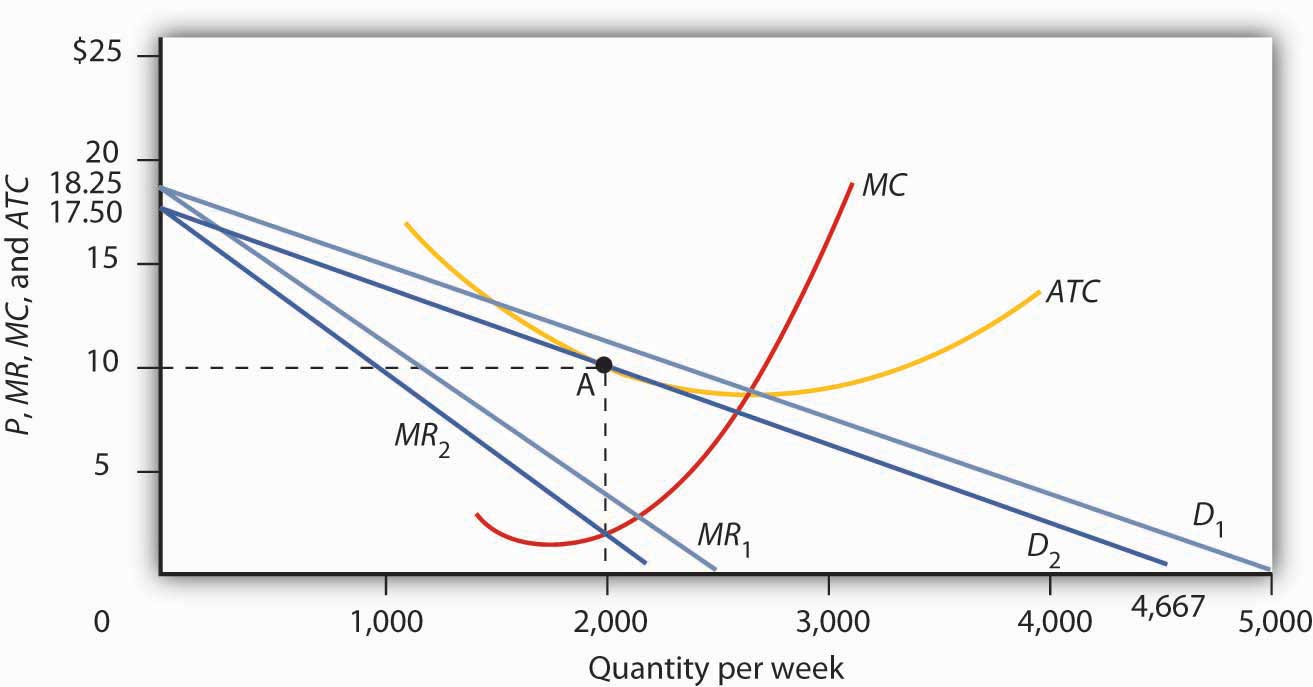 Monopolistic Competition Competition Among Many
Monopolistic Competition Competition Among Many
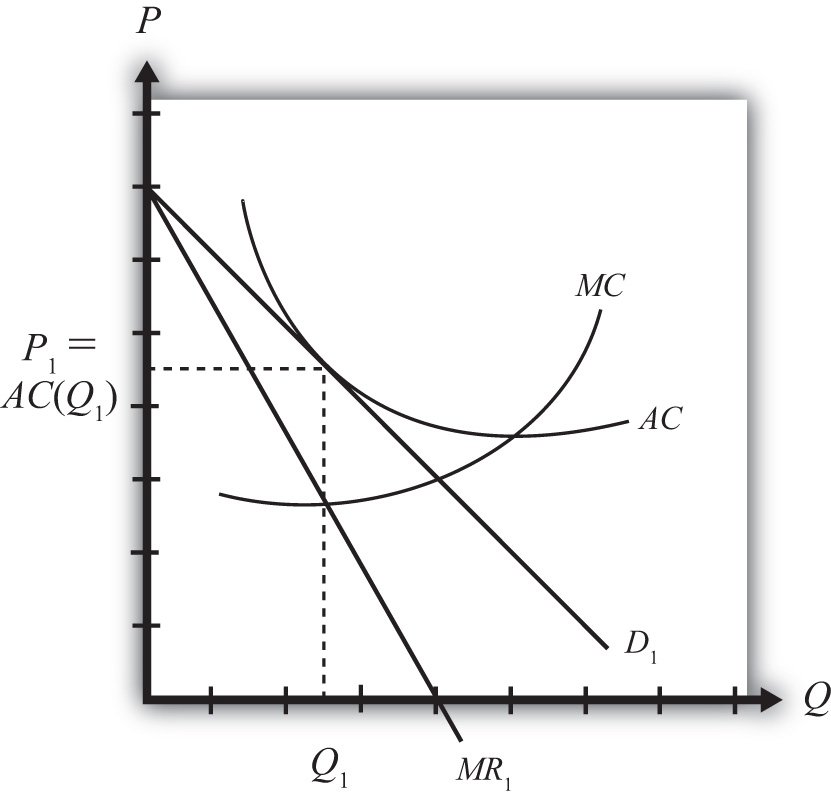 The Effects Of Trade In A Monopolistically Competitive Industry
The Effects Of Trade In A Monopolistically Competitive Industry

Trade Chapter 80 5b The Effects Of Trade In A Monopolistically
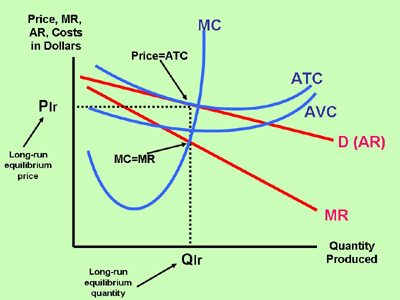 Section 2 Short Run And Long Run Profit Maximization For A Firm In
Section 2 Short Run And Long Run Profit Maximization For A Firm In
 Animated Diagram Showing A Firm In A Monopolistically Competitive
Animated Diagram Showing A Firm In A Monopolistically Competitive
0 Response to "The Monopolistically Competitive Firm In The Diagram Is"
Post a Comment