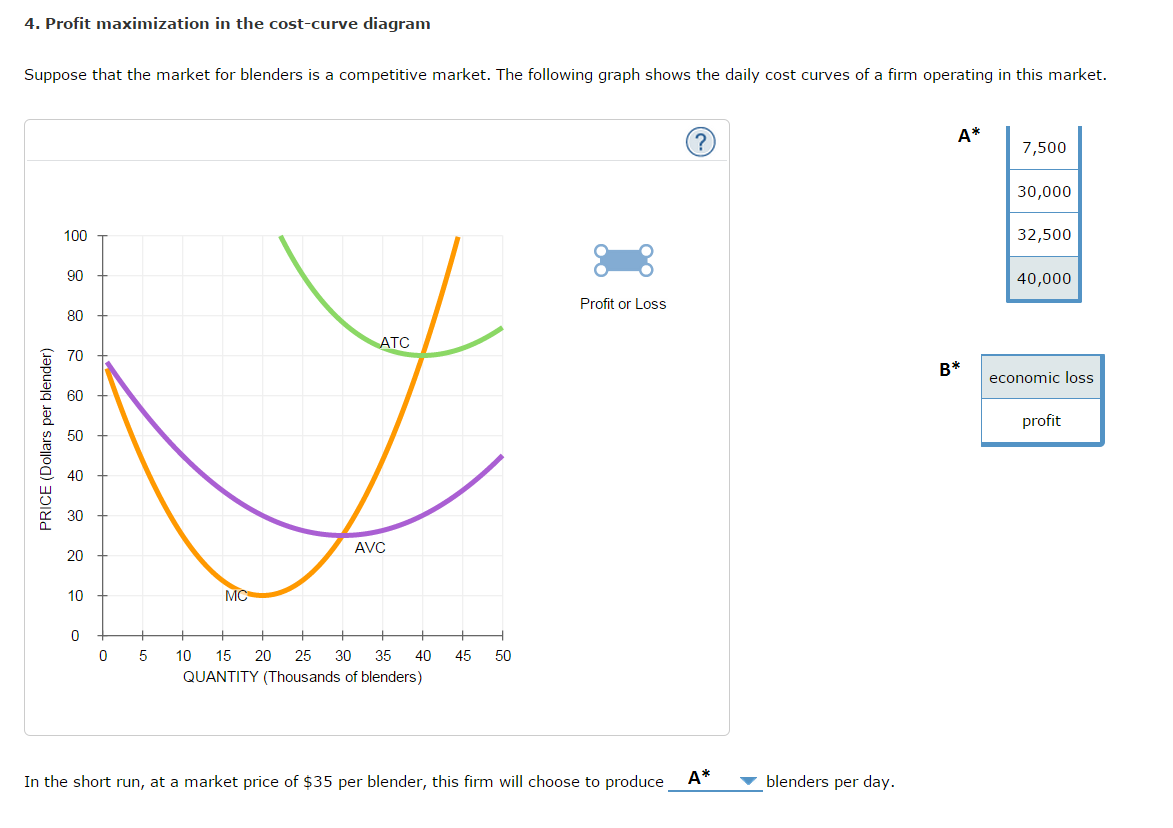
4 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram
Suppose that the market for cashmere sweaters is a competitive market. This is the end of the preview.
 Reading Illustrating Monopoly Profits Microeconomics
Reading Illustrating Monopoly Profits Microeconomics
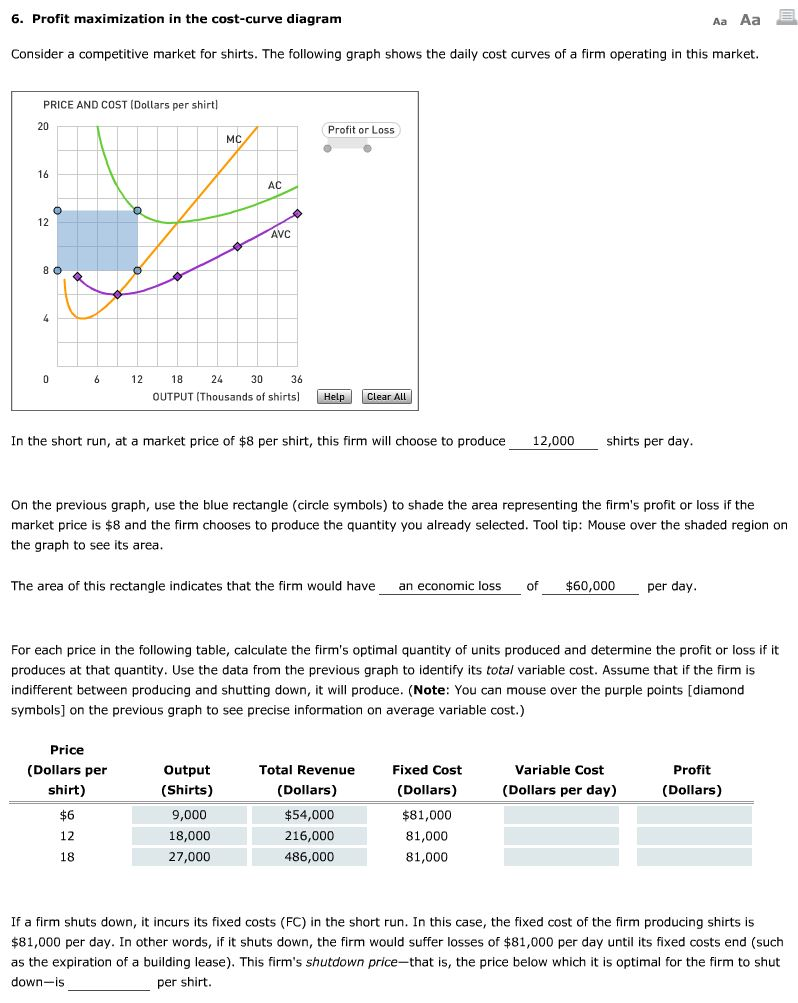
The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market.

4 profit maximization in the cost curve diagram. Suppose that the market for blenders is a competitive market. In the short run at a market price of 80 per sweater this firm will choose to produce on the previous graph. The entrepreneur is the sole owner of the firm.
An economic profit equal to zero. Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram suppose that the market for candles is a competi. Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram 3 profit.
Sign up to view the full version. Sign up to access the rest of the document. This is the end of the preview.
Sign up to access the rest of the document. Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram. Total costs will be the quantity of 90 times the average cost of 350 which is shown by the area of the rectangle from the origin to a quantity of 90 up to point c over to the vertical axis and down to the origin.
It is an economic profit just high enough to keep a firm engaged in its current activity. Now that we know how to find the profit maximization point were going to show the amount of profit on the diagram using the average cost curve. On the previous graph use the blue rectangle circle symbols to shade the area representing the firms profit or loss if.
Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram. Therefore if this firm chooses to produce sweaters it will produce 8000 sweaters per day the quantity at which marginal cost is equal to the price of 15 per sweater. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market.
Techniques of production are given. Profit maximization in the cost curve diagram a3 consider a perfectly competitive market for frying pans. Tastes and habits of consumers are given and constant.
The profit maximisation theory is based on the following assumptions. So as i said in the last lecture average cost is the cost per unit of output. Assume that the market for frying pans is a competitive market and the market price is 20 per frying pan.
The objective of the firm is to maximise its profits where profits are the difference between the firms revenue and costs. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. In the short run at a market price of 20 per candle this firm will choose to produce candles per day.
The average cost of producing 90 packs is shown by point c or about 350. This preview has intentionally blurred sections. Profits and losses with the average cost curve.
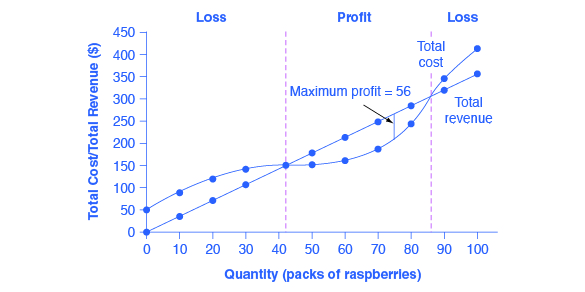 8 2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions
8 2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions
 Orange Micro Chapter 14 Firms In Competitive Markets
Orange Micro Chapter 14 Firms In Competitive Markets
 Perfect Competition Long Run Intelligent Economist
Perfect Competition Long Run Intelligent Economist

 2 Supply Curves Estimated For Three Public Forest Scenarios 1
2 Supply Curves Estimated For Three Public Forest Scenarios 1
 Profits Profit Maximisation Economics Online
Profits Profit Maximisation Economics Online
Amosweb Is Economics Encyclonomic Web Pedia
Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Elegant Top 3 Theories
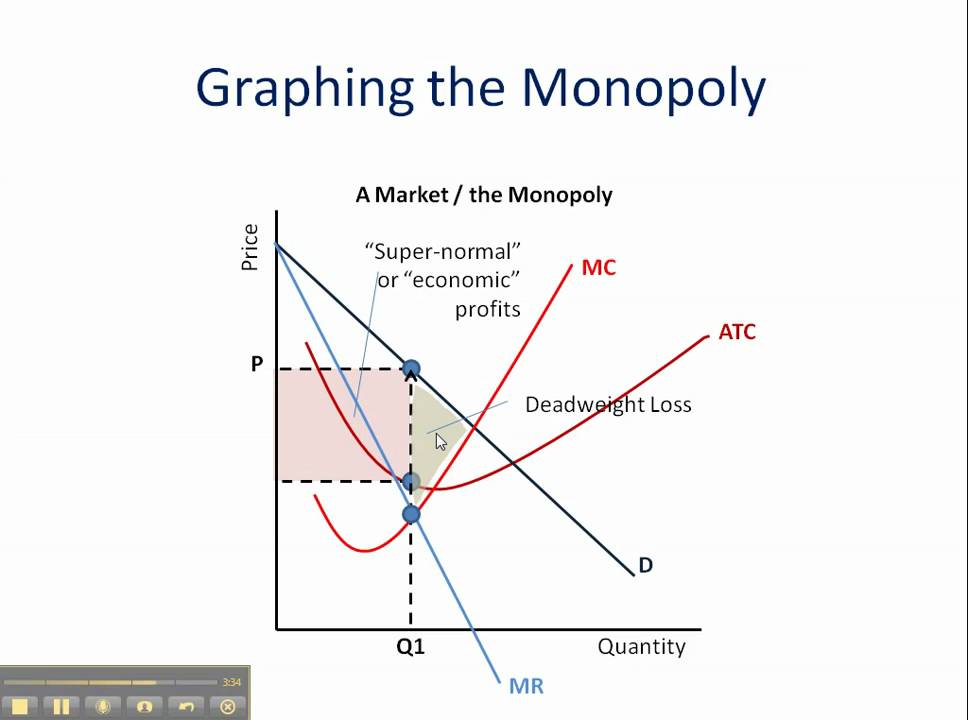 Monopoly How To Graph It Youtube
Monopoly How To Graph It Youtube
 Gottheil Quiz Price And Output
Gottheil Quiz Price And Output

 Solved 6 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram C
Solved 6 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram C
 Profit Maximisation Meaning Producers Equilibrium Mc Mr Approach
Profit Maximisation Meaning Producers Equilibrium Mc Mr Approach
 Price Discrimination Maximising Profits Using Different Prices
Price Discrimination Maximising Profits Using Different Prices
 Satisficing Behaviour By Businesses Tutor2u Economics
Satisficing Behaviour By Businesses Tutor2u Economics
 Aplia Student Question 17 4 Correctanswer 50 45 Profitorloss
Aplia Student Question 17 4 Correctanswer 50 45 Profitorloss
 Reading Illustrating Monopoly Profits Microeconomics
Reading Illustrating Monopoly Profits Microeconomics
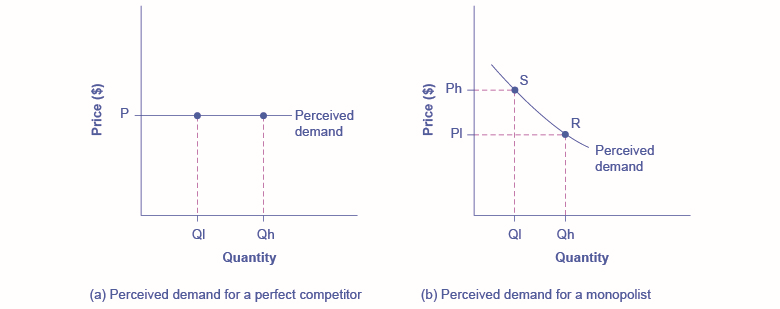 9 2 How A Profit Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output And Price
9 2 How A Profit Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output And Price

Amosweb Is Economics Encyclonomic Web Pedia
 Solved Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Supp
Solved Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram Supp
0 Response to "4 Profit Maximization In The Cost Curve Diagram"
Post a Comment